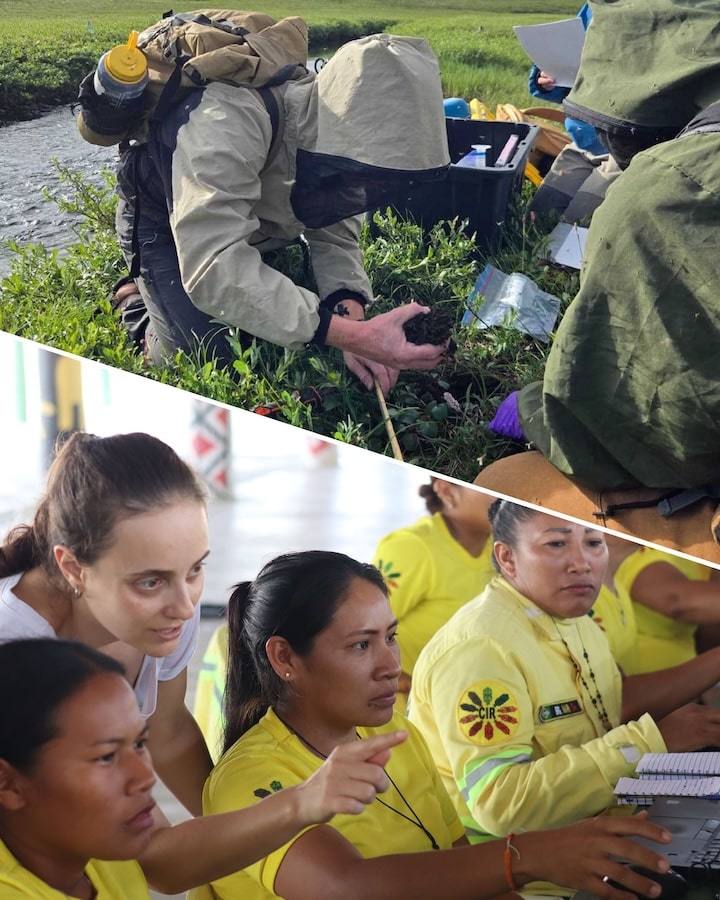
Ecological warning lights have blinked on across the Arctic over the last 40 years, according to new research, and many of the fastest-changing areas are clustered in Siberia, the Canadian Northwest Territories, and Alaska. The analysis of the rapidly warming Arctic-boreal region, published in Geophysical Research Letters this week, provides a zoomed-in picture of ecosystems experiencing some of the fastest and most extreme climate changes on Earth.
Many of the most climate-stressed areas featured permafrost, or ground that stays frozen year-round, and experienced both severe warming and drying in recent decades.
To identify these “hotspots,” a team of researchers from Woodwell Climate Research Center, the University of Oslo, the University of Montana, the Environmental Systems Research Institute (Esri), and the University of Lleida used more than 30 years of geospatial data and long-term temperature records to assess indicators of ecosystem vulnerability in three categories: temperature, moisture, and vegetation.
Building on assessments like the NOAA Arctic Report Card, the research team went beyond evaluating isolated metrics of change and looked at multiple variables at once to create a more complete, integrated picture of climate and ecosystem changes in the region.
“Climate warming has put a great deal of stress on ecosystems in the high latitudes, but the stress looks very different from place to place and we wanted to quantify those differences,” said Dr. Jennifer Watts, Arctic program director at Woodwell Climate and lead author of the study. “Detecting hotspots at the local and regional level helps us not only to build a more precise picture of how Arctic warming is affecting ecosystems, but to identify places where we really need to focus future monitoring efforts and management resources.”
The team used spatial statistics to detect “neighborhoods,” or regions of particularly high levels of change during the past decade.
“This study is exactly why we have developed these kinds of spatial statistic tools in our technology. We are so proud to be working closely with Woodwell Climate on identifying and publishing these kinds of vulnerability hotspots that require effective and immediate climate adaptation action and long-term policy,” said Dr. Dawn Wright, chief scientist at Esri. “This is essentially what we mean by the ‘Science of Where.’”
The findings paint a complex and concerning picture.
The most substantial land warming between 1997-2020 occurred in the far eastern Siberian tundra and throughout central Siberia. Approximately 99% of the Eurasian tundra region experienced significant warming, compared to 72% of Eurasian boreal forests. While some hotspots in Siberia and the Northwest Territories of Canada grew drier, the researchers detected increased surface water and flooding in parts of North America, including Alaska’s Yukon-Kuskokwim Delta and central Canada. These increases in water on the landscape over time are likely a sign of thawing permafrost.
Among the 20 most vulnerable places the researchers identified, all contained permafrost.
“The Arctic and boreal regions are made up of diverse ecosystems, and this study reveals some of the complex ways they are responding to climate warming,” said Dr. Sue Natali, lead of the Permafrost Pathways project at Woodwell Climate and co-author of the study. “However, permafrost was a common denominator—the most climate-stressed regions all contained permafrost, which is vulnerable to thaw as temperatures rise. That’s a really concerning signal.”
For land managers and other decisionmakers, local and regional hotspot mapping like this can serve as a more useful monitoring tool than region-wide averages. Take, for instance, the example of Covid-19 tracking data: maps of county-by-county wastewater data tend to be more helpful tools to guide decision making than national averages, since rates of disease prevalence and transmission can vary widely among communities at a given moment in time. So, too, with climate trends: local data and trend detection can support management and adaptation approaches that account for unique and shifting conditions on the ground.
The significant changes the team detected in the Siberian boreal forest region should serve as a wakeup call, said Watts. “These forested regions, which have been helping take up and store carbon dioxide, are now showing major climate stresses and increasing risk of fire. We need to work as a global community to protect these important and vulnerable boreal ecosystems, while also reining in fossil fuel emissions.”
Explore these 15 maps by award-winning Woodwell Climate cartographers Greg Fiske and Christina Shintani. Created in 2024, each tells a story about the immense beauty of the high north, the dramatic changes unfolding as the Arctic continues to warm three to four times faster than the rest of the world, and the equitable solutions being developed to address climate impacts in the region
Read More on Permafrost Pathways.
A chapter of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) 2024 Arctic Report Card, published today, presents a new, comprehensive pan-Arctic carbon assessment that, when accounting for wildfire emissions, finds that the Arctic tundra has shifted from storing carbon to being a source of carbon emissions to the atmosphere.
While the Arctic has been a carbon “sink” for thousands of years—storing more carbon than it releases—the Arctic Report Card chapter, Arctic Terrestrial Carbon Cycling, explores how rapid Arctic warming is prompting a range of ecosystem changes that are leading to increased emissions throughout the region. Among these are thawing permafrost (perennially frozen ground), wildfires, and plant and microbial changes.
In particular, the assessment, led by scientists at Woodwell Climate Research Center, finds that 2024 marked the second-warmest average yearly permafrost temperatures on record for Alaska, and the second-highest year for wildfire emissions north of the Arctic Circle.
“The Arctic is warming up to four times the global rate, and we need accurate, holistic, and comprehensive knowledge of how climate changes will affect the amount of carbon the Arctic is taking up and storing, and how much it’s releasing back into the atmosphere, in order to effectively address this crisis,” said Dr. Sue Natali, Woodwell Climate scientist, chapter lead and lead of Woodwell Climate’s Permafrost Pathways project. “This report represents a critical step toward quantifying these emissions at scale which is critical for understanding their impacts on global climate and informing equitable mitigation and adaptation strategies.”
“In recent years, we’ve seen how increasing fire activity from climate change threatens both communities and the carbon stored in permafrost, but now we’re beginning to be able to measure the cumulative impact to the atmosphere, and it’s significant,” said Dr. Brendan Rogers, Woodwell Climate scientist, chapter co-author, and co-lead of Woodwell Climate’s Permafrost Pathways project.
“This year’s report demonstrates the urgent need for adaptation as climate conditions quickly change,” said Twila Moon, lead editor of the 2024 Arctic Report Card and deputy lead scientist at the National Snow and Ice Data Center. “Indigenous Knowledge and community-led research programs can inform successful responses to rapid Arctic changes.”
Contributions to the chapter were also made by Woodwell Climate scientists, Dr. Kyle Arndt, Dr. Jacqueline Hung, Greg Fiske, Stefano Potter, and Dr. Anna Virkkala, as well as collaborators at University of Alaska-Fairbanks, Northern Arizona University, and Université de Montréal.
The Arctic Report Card combines the best available research from over 97 scientists from 11 countries, including seven from Woodwell Climate. Its chapters reveal record-setting observations of a rapidly warming Arctic, including rising air temperatures, declines of large inland caribou herds, and increasing precipitation. These climate impacts and others threaten the health, subsistence, and homes of many Indigenous communities living in the Arctic.
The full Arctic Report Card can be read here.
“What if you’re not on the map?”
Dr. Kelsey Leonard of the Shinnecock Indian Nation addressed this question to a room of Geographic Information System (GIS) professionals at Esri’s global mapping conference in 2023. Leonard, who uses maps to advance Indigenous water justice, asks this question to raise awareness about the absence of Indigenous land and languages in GIS tools. The removal of traditional place names in physical spaces, cartographic maps, and geospatial software often contributes to the erasure of Indigenous culture and history.
The Permafrost Pathways project, like Leonard, is working to change that.
Read more on Permafrost Pathways
A new study, published in Nature Communications Earth and Environment and co-authored by researchers at Atmospheric and Environmental Research, Inc. (AER) and Woodwell Climate Research Center, finds that abnormally warm temperatures in the Arctic are associated with a higher likelihood of severe winter weather including cold-air outbreaks and heavy snowfall in Northern Hemisphere continents.
“When the Arctic atmosphere is warmer than normal, we see a much higher likelihood of extreme winter weather across much of Canada, the northern U.S. and northern Eurasia,” remarked lead author, Dr. Judah Cohen at AER. “The relationship is especially strong in the northeastern sections of the continents.”
“Even though we’re seeing cold records being broken less often as the globe warms, we’ll still see debilitating spells of severe winter weather,” added co-author Dr. Jennifer Francis at Woodwell Climate. “There will be plenty of ice, snow, and frigid air in the Arctic winter for decades to come, and that cold can be displaced southward into heavily populated regions during Arctic heat waves.”
Recent disruptive extreme winter weather events—such as the deadly Texas cold spell of February 2021—have occurred and will continue to occur in the future, wreaking havoc on infrastructure, human wellbeing, and ecosystems, especially in areas unaccustomed to and ill-equipped for dealing with winter extremes.
“The Arctic may seem irrelevant and far away to most folks, but our findings say the profound changes there are affecting billions of people around the Northern Hemisphere,” added Dr. Francis. To reverse these trends, “it will take bold and rapid actions to reduce our burning of fossil fuels and the build-up of heat-trapping gasses in the atmosphere, but the tools exist if we can muster the will.”
According to Francis, recent studies have theorized that rapid Arctic warming, a pace three-to-four times faster than the globe as a whole, may increase the likelihood of extreme weather events owing to a reduced north/south temperature difference. In addition, slower westerly winds of the jet stream lead to more frequent convoluted jet-stream configurations, which lead to unusual weather.
“Disruptions in the typically stable stratospheric polar vortex may also occur more often in a warming climate,” noted Cohen, “and we know hazardous winter weather is more likely during these disruptions.”
Fire is a necessary element in northern forests, but with climate change, these fires are shifting to a far less natural regime— one that threatens the ecosystem instead of nurturing it.
Boreal tree species, like black spruce, have co-evolved over millennia with a steady regime of low-frequency, high-intensity fires, usually ignited by lightning strikes. These fires promote turnover in vegetation and foster new growth. On average, every 100 to 150 years, an intense “stand-replacing” fire might completely raze a patch of forest, opening a space for young seedlings to take root.
But rapid warming in northern latitudes has intensified this cycle, sparking large fires on the landscape more frequently, jeopardizing regeneration, and releasing massive amounts of carbon that will feed additional warming. Here’s how climate change is impacting boreal fires.
Climate Impacts on Boreal Fire
In order for a fire to start, you need three things— favorable climatic conditions, a fuel source, and an ignition source. These elements, referred to as the triangle of fire, are all being exacerbated as boreal forests warm, resulting in a fire regime with much larger and more frequent fires than the forests evolved with.
Climate conditions
Forest fires only ignite in the right conditions, when high temperatures combine with dryness in the summer months. As northern latitudes warm at a rate three to four times faster than the rest of the globe, fire seasons in the boreal have lengthened, and the number of fire-risk days have increased.
In some areas of high-latitude forest, climate change has changed the dynamics of snowfall and snow cover disappearance. The rate of spring snowmelt is often an important factor in water availability on a landscape throughout the summer. A recent paper, led by Dr. Thomas Hessilt of Vrije University in collaboration with Woodwell Associate Scientist, Dr. Brendan Rogers, found that earlier snow cover disappearance resulted in increased fire ignitions. Early snow disappearance was also associated with earlier-season fires, which were more likely to grow larger— on average 77% larger than historical fires.
Fuel
The second requirement for fires to start is available “fuel”. In a forest, that’s vegetation (both living and dead) as well as carbon-rich soils that have built up over centuries. Here, the warming climate plays a role in priming vegetation to burn. A paper co-authored by Rogers has demonstrated temperatures above approximately 71 F in the forest canopy can be a useful indicator for the ignition and spread of “mega-fires,” which spread massive distances through the upper branches of trees. The findings suggest that heat-stressed vegetation plays a big role in triggering these large fires.
Warming has also triggered a feedback loop around fuel in boreal systems. In North America, the historically dominant black spruce is struggling to regenerate between frequent, intense fires. In some places, it is being replaced by competitor species like white spruce or aspen, which don’t support the same shaded, mossy environment that insulates frozen, carbon-rich soils called permafrost, making the ground more vulnerable to deep-burning fires. When permafrost soils thaw and burn, they release carbon that has been stored—sometimes for thousands of years—contributing to the acceleration of warming.
Ignition
Finally, fires need an ignition source. In the boreal, natural ignitions from lightning are the most frequent culprit, although human-caused ignitions have become more common as development expands into northern forests.
Because of lightning’s ephemeral nature, it has been difficult to quantify the impacts of climate change on lightning strikes, but recent research has shown lightning ignitions have been increasing since 1975, and that record numbers of lightning ignitions correlated with years of record large fires. Some models indicate summer lightning rates will continue to increase as global temperatures rise.
There is also evidence showing that a certain type of lightning— one more likely to result in ignition— has been increasing. This “hot lightning” is a type of lightning strike that channels an electrical charge for an extended period of time and tends to correlate more frequently with ignitions. Analysis of satellite data suggests that with every one degree celsius of the Earth’s warming, there might be a 10% increase in the frequency of these hot lightning strikes. That, coupled with increasingly dry conditions, sets the stage for more frequent fire ignitions.
Fire Management as a Climate Solution
So climate change is intensifying every side of the triangle of fire, and the combined effects are resulting in more frequent, larger, more intense blazes that contribute more carbon to the atmosphere. While the permanent solution to bring fires back to their natural regimes lies in curbing global emissions, research from Woodwell Climate suggests that firefighting in boreal forests can be a successful emissions mitigation strategy. And a cost effective one too— perhaps as little as $13 per metric ton of carbon dioxide avoided, which puts it on par with other carbon mitigation solutions like onshore wind or utility-scale solar. It also has the added benefit of protecting communities from the health risk of wildfire smoke.
Rogers, along with Senior Science Policy Advisor, Dr. Peter Frumhoff, and Postdoctoral researcher Dr. Kayla Mathes have begun work in collaboration with the Yukon Flats National Wildlife Refuge in Alaska to pilot this solution as part of the Permafrost Pathways project. Yukon Flats is underlain by large tracts of particularly carbon-rich permafrost soils, making it a good candidate for fire suppression tactics to protect stored carbon.
The project will be the first of its kind— working with communities in and around the Refuge as well as US agencies to develop and test best practices around fighting boreal fires specifically to protect carbon. Broadening deployment of fire management could be one strategy to mitigate the worst effects of intensifying boreal fires, buying time we need to get global emissions in check.
What are ice wedges, and why are they important to climate change?
“I think ice wedges are what make permafrost interesting,” says Dr. Anna Liljedahl.
Liljedahl works on Woodwell Climate’s Arctic team as an Associate Scientist. She aims to understand how climate change is affecting water storage and movement. Much of her recent work focuses on ice wedges and how they are reacting to warming Arctic summers. But just what are ice wedges anyway?
Ice wedges are one of the three main features of the Arctic’s land surface. Permafrost, ground that remains below 0˚C for at least two consecutive summers, lies under a thinner layer of thawing and refreezing soil, called the active layer. When permafrost cracks during cold winter days, snowmelt and runoff water seep into the empty space. These eventually freeze and create a wedge-shaped spear of ice that extends vertically down into the permafrost.
Ice wedges actively re-shape the tundra. When they freeze, they grow and expand outward, pushing against the bordering permafrost and active layer. With nowhere else to go, permafrost and soil push upwards, and ridges form on the surface of the tundra. The ridges interlock and form distinct shapes, referred to as ice-wedge polygons.
The ridged borders of ice-wedge polygons form directly above expanding ice wedges below the surface, and are therefore more elevated. The lower internal portion of the polygon allows pools of water from runoff and snowmelt to form atop the active layer. These polygons are visible all the way from space.
Thanks to satellite imagery, scientists like Liljedahl are able to monitor ice-wedge polygons remotely. Satellite images date back to the mid-20th century and can be used to observe changes in the landscape overtime.
During unusually warm summers, the tops of ice wedges can melt, which removes underlying support of the ground surface, causing slumps along the borders of ice-wedge polygons. These leveling borders form channels that siphon the water from pools in the centers of neighboring polygons. The resulting runoff streams can drain small pools and even larger lakes that took thousands of years to form.
With the progression of climate change, these drainage systems have become more common. Liljedahl refers to them in the title of her manuscript, just published in the July issue of Nature Water, “The Capillaries of the Arctic Tundra.”
The increase in creation of new “capillaries” in the Arctic is impacting not only the topographical landscape of the region, but also the livelihoods of all beings that find their home there.
At first, the melt of these ice wedges can spark an uptick in the variation of vegetation due to moisture along the sides of the channel. This, however, is temporary. When the ice wedges stabilize again in the winter, this variation decreases once more.
Aquatic mosses— one of the most productive vegetal forms in the Arctic, equivalent in productivity to Arctic shrubs— inhabit pools formed alongside the edges of ice-wedge polygons. They lose their homes when bodies of water drain away. Major vegetation changes can alter carbon storage, availability, and emissions across the tundra.
Humans are also impacted. Homes become too dangerous to live in as the ground supporting vital infrastructure collapses. Roads connecting communities to important resources are destroyed by subsiding ground.
Despite their widespread impact, ice wedges are often overlooked in Arctic climate models. Historically, their inclusion “costs too much computer time,” Liljedahl says, to factor in. Many climate models take a holistic approach to the Arctic landscape, as opposed to focusing on smaller details.
To remedy this, Liljedahl suggests utilization of developing technology such as Artificial Intelligence (AI). Classifying the Arctic landscape by type, for example, into high-center polygons, low-center polygons, and capillary networks, would factor ice wedge change into climate models. As AI advances and becomes a more common research tool, it could help decrease the human computing time that Liljedahl identifies as a barrier.
Arctic research is likely to change drastically in the coming years. With new technologies, and as we learn more about the Arctic landscape, research models will likely become more inclusive of the varied features within it, and much more accurate.
“There are exciting years ahead,” Liljedahl says, “I think we’re going to see some cool stuff coming out [of tundra research] in the next five to ten years.”
The exhibit “In Flux: Perspectives on Arctic Change” sprawls across two floors of one of Cape Cod’s oldest summer-home mansions— Highfield Hall.
When they first walk in, visitors see two of Woodwell Climate Board Member Georgia Nassikas’ encaustic paintings flanking a banner with the name of the exhibit. Woodwell Senior Geospatial Analyst Greg Fiske’s maps light up the entry hall. Sounds from Michaela Grill and Karl Lemiuex’s documentary film cascade down from the staircase to the second floor. Tall windows illuminate Gabrielle Russomagno’s small, detailed photographs of the Arctic’s durable vegetation and Aaron Dysart’s reflective sculpture, which invites us to tread with caution.
These six artists’ works have been on display in Highfield Hall since May 21st, and will remain as part of the “In Flux” exhibit until July 14th. On July 11th, some of the artists will participate in a panel discussion with their Woodwell scientist collaborators, Dr. Jennifer Watts and Dr. Sue Natali.
Connecting to a new perspective
The exhibit’s goal is to connect a distant community to the reality of Arctic change. Many of us may never have the opportunity to visit the Arctic, or study it like Woodwell Climate researchers do. Art can help communicate the reality of an unfamiliar place.
Woodwell Climate’s Arctic research informed every piece of art on display at Highfield Hall. Each artist has had the chance to travel to the Arctic alongside Woodwell researchers Dr. Jenny Watts and Dr. Sue Natali. According to Watts, traveling with an artist brought a new perspective to a landscape she had visited so many times before.
“They are looking through the lens of the artist,” Watts says, “They’re kind of seeing it through this fresh look, and then we’re able to see it through their eyes.”
Russomagno calls herself a “student of the Arctic.” Like some of the other artists, she had never been so far north before her 5-day trip with Watts to Alaska. She recalled the whirlwind experience of creating while acclimating to her new surroundings.
“I was able to be making art while discovering,” Russomagno says, “I was looking at the same material [as Watts] and understanding it completely differently.”
The exhibit assumes visitors might come in with certain assumptions about the Arctic, but hopes they will soon throw their preconceived ideas out of Highfield Hall’s many windows. One of these false ideas, Watts says, is that the Arctic is a barren wasteland.
“In the summer especially, it’s brimming with life, and we wanted to show that part of the story because it’s often overlooked,” she says.
Bursts of life from the summer tundra— small shrubs, mosses, lichens, and grasses— are featured in Russomagno’s series of photographs in “The Quiet & the Mighty.” Nassikas’ encaustic paintings uniquely depict color, horizon, and change. Fiske’s maps teleport us from Highfield Hall to the tundra. The entire “In Flux” exhibit displays unexpected dimension.
Why combine art and science?
The experience of the art at Highfield places the viewer in the atmosphere of the Arctic tundra. A quiet place with unexpected vibrancy, the uptick in frequency of deafening crashes as ice melts, breaks, and shifts. These elements would be much harder to glean from traditional methods of communication in the science world. A graph, for example, would likely not evoke such a strong emotional response.
“I think Woodwell and other science organizations struggle with conveying their data, and hard facts, and things they’re discovering to a general audience,” Nassikas says, “Art is another way to change the world for the better.”
Dysart echoed this message: “If research does not connect with people and culture, nothing’s going to change. Art can make that connection. Art has strength that words don’t.”
Our shared home
Part of the power of this exhibit is its setting. We have the opportunity to experience the Arctic’s dynamic changes outside of its natural barriers, and Highfield Hall is the tether.
Dysart says it is “A call back to [our] normal life as opposed to the gallery aesthetic.”
Highfield is a home. It may not feel familiar to everyone, with its extravagant furnishings, stained glass windows, chandeliers, and many rooms, but it was built by humans, for humans. The house has withstood the test of time, though it has changed greatly since its construction in 1878. The Arctic, too is a home for many people, animals, and plants— one that is threatened by climate change. The exhibit at Highfield Hall brings the changing Arctic home to our own changing landscape.